Email us:
info@andrea-digestive-clinic.comCall us:
+65 6264-2836#21-11/12 Royal Square Medical Centre
Mon - Fri : 9am - 5pm, Sat : 9am - 1pm
If you often experience bloating, gas or unpredictable bowel habits despite watching your diet, then you could be dealing with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), a condition where too many bacteria grow in the small intestine, disrupting digestion. The good news is that with proper medical evaluation and targeted treatment, SIBO can be effectively managed, helping you regain digestive comfort and energy.
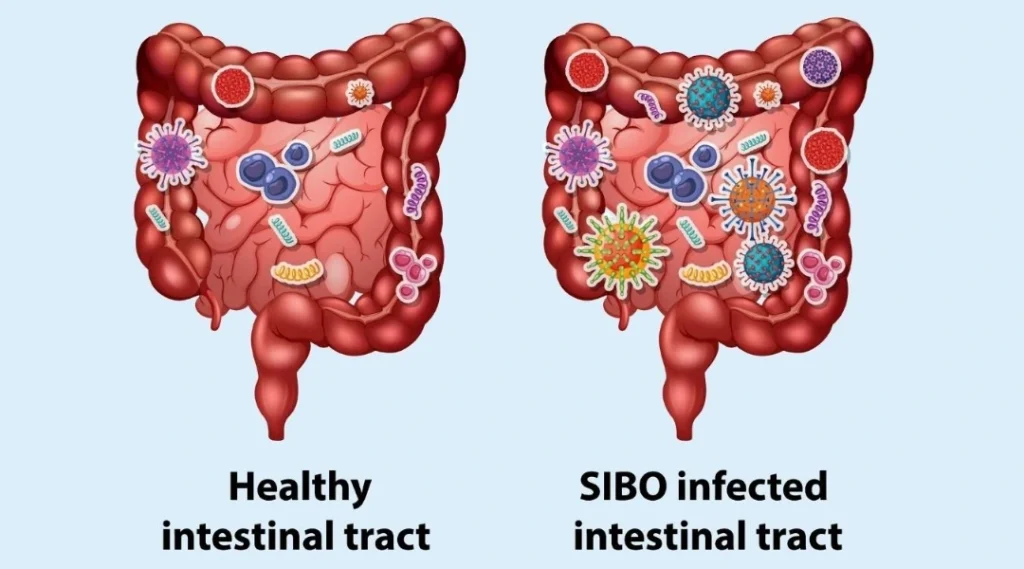
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth occurs when bacteria that usually reside in the large intestine migrate into or excessively multiply within the small intestine. These bacteria ferment carbohydrates prematurely, producing gases and by-products that disrupt normal digestion and irritate the intestinal lining.
Over time, this abnormal bacterial activity can impair the absorption of essential nutrients, such as vitamin B12, iron and fat-soluble vitamins. Unlike temporary digestive upset, SIBO often requires medical assessment to identify underlying contributors and guide treatment, as recurrence is common if root causes are not addressed.
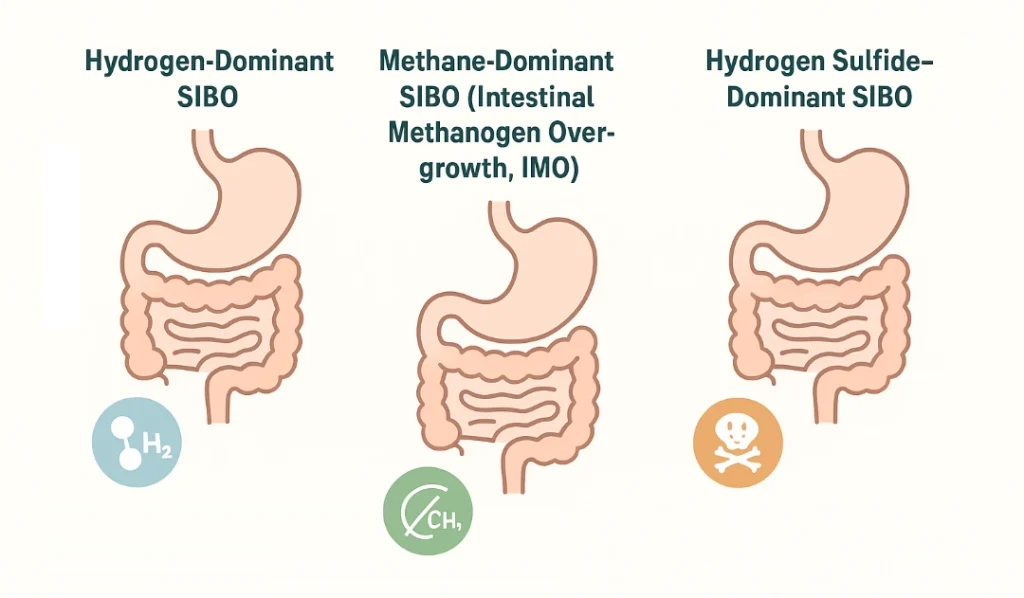
The condition can be classified based on the predominant gas produced during bacterial fermentation, which often correlates with symptom patterns. This includes:
This is the most common type and is typically associated with diarrhoea, loose stools and urgency. Symptoms often worsen after carbohydrate-rich meals.
Methane production is more commonly linked to constipation, bloating and slow gut transit. Despite the name, methanogens are not bacteria but microorganisms that thrive in similar conditions.
This subtype may cause foul-smelling gas, abdominal pain and diarrhoea. It is less commonly tested for but increasingly recognised in patients with persistent symptoms.
SIBO typically develops when normal intestinal defence mechanisms are disrupted, allowing bacteria to accumulate in the small intestine. These contributors can broadly be grouped into underlying causes and predisposing risk factors.

Symptoms of SIBO can vary depending on the type and severity of overgrowth, but often include:
In more advanced cases, nutrient malabsorption may lead to vitamin deficiencies and unintended weight loss.
A timely identification of SIBO allows treatment to be targeted and helps minimise recurrence. The evaluation typically combines clinical assessment with specialised testing, such as:
Managing SIBO requires a structured and individualised approach that addresses both symptoms and underlying causes. This typically entails:

Medical assessment is recommended if you experience any of the following:

Managing small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) often involves understanding what lies beyond an initial diagnosis. Many individuals seeking care already have clarity from prior investigations and are now looking for practical, next-step guidance on managing symptoms and preventing recurrence.
At our clinic, Dr Andrea Rajnakova’s care extends beyond procedures alone. The consultations take a thorough and structured approach, exploring gut motility, dietary patterns, lifestyle factors, medical history and previous treatments that may contribute to bacterial overgrowth. This broader perspective allows management plans to be tailored to how SIBO affects each individual’s daily function, energy levels and nutritional health.
As the only gastroenterology clinic in Singapore with an in-house dietitian, Ms Veronica Cavallini, medical and dietary strategies are aligned from the outset. This close collaboration between Dr Andrea and Ms Veronica supports sustainable symptom control, preserves nutritional balance and helps patients avoid unnecessary long-term dietary restriction.
For patients experiencing persistent or recurring gut symptoms, clarity around contributing factors is often the next step. Our clinic offers a structured and individualised approach to SIBO management, tailored to your clinical context and long-term digestive health. Contact us to arrange a consultation session and receive a personalised treatment plan.
Is SIBO the same as IBS?
No. While SIBO and IBS share similar symptoms, SIBO involves bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine and may be an underlying contributor to IBS symptoms in some individuals.
Can SIBO be cured?
SIBO can be treated effectively, but recurrence is possible if underlying causes are not addressed. Long-term management focuses on prevention as well as symptom control.
Is SIBO serious?
If it is untreated, SIBO can cause nutrient deficiencies, weight loss and reduced quality of life, but early treatment significantly lowers these risks.
Do I need antibiotics for SIBO?
Many patients require antibiotics as part of treatment, but they are usually combined with dietary strategies and management of contributing factors.
Can SIBO come back after treatment?
Yes, recurrence can occur. Ongoing management of gut motility, diet and underlying conditions is important to reduce relapse risk.
